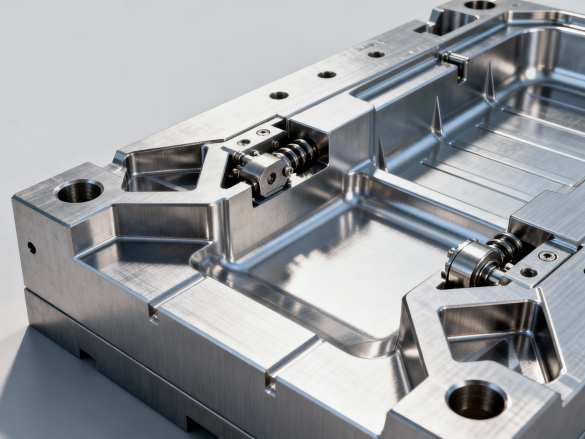
In the fast-paced world of vehicle development, particularly with the surge of Electric Vehicles (EVs), the race to market is relentless. Engineers and procurement managers face a critical challenge: validating designs quickly without committing to the immense cost and lead time of production molds. Automotive injection molding serves as the backbone of this process, offering a spectrum of solutions from rapid prototyping to mass production. Whether developing complex connectors or aesthetic interior components, selecting the right tooling strategy is essential for reducing risks and accelerating iteration cycles.
Strategic Material Selection for Automotive Tooling Efficiency
Selecting the optimal mold material is pivotal for balancing budget constraints with the urgent need for functional validation in modern vehicle development programs.
Comparing Aluminum and Steel for Prototype Durability
The choice between rapid tooling materials and traditional steel defines the timeline and success of early-stage testing. Aluminum 7075 and soft steels like P20 are the standard for rapid tooling, offering a significant speed advantage. Aluminum molds, for instance, can be machined 30% to 50% faster than hardened tool steel, allowing engineers to receive functional “injection molding automotive parts” in days rather than months.
However, durability varies significantly. An aluminum mold is typically rated for 1,000 to 5,000 cycles, making it ideal for fit-and-finish checks or crash test batches. In contrast, traditional hardened steel molds are designed for the plastic injection molding automotive industry’s mass production needs, capable of withstanding over one million cycles. For example, a dashboard component requiring a high-gloss finish and textured grain would necessitate the thermal stability of steel for long-term consistency, whereas a hidden structural bracket for an initial EV battery prototype is perfectly suited for aluminum tooling.
Optimizing Cost-Benefit Ratios for Verification Batches
Financial efficiency is a major driver in the shift toward rapid tooling for low-volume runs. Committing to a Class A production mold for a component that has not yet been finalized is a high-risk investment. Rapid tooling acts as a “bridge,” allowing manufacturers to produce verification batches at a fraction of the cost.
Data from recent automotive projects suggests that utilizing bridge tooling for the first 500 units can reduce upfront capital expenditure by approximately 40% compared to cutting a full production tool immediately. This approach allows R&D teams to identify geometry issues—such as interference in snap-fits—and modify the easier-to-machine soft mold before the design is frozen. Once the design is validated, the heavy investment in an automotive injection mold made of hardened steel becomes a calculated, safe decision rather than a gamble, ensuring the ROI remains positive throughout the vehicle’s lifecycle.
Technological Integration in High-Precision Manufacturing
Modern automotive production utilizes scientific molding protocols and advanced simulation to ensure part consistency and reduce defects before mass manufacturing begins.
Ensuring Process Stability via Scientific Molding
The transition from “art to part” has evolved into a data-driven science. Leading automotive injection molding suppliers now rely on Decoupled Molding strategies rather than operator intuition. By separating the filling, packing, and holding phases, manufacturers gain precise control over the polymer’s behavior inside the mold.
For instance, in the production of safety-critical automotive rubber injection molding parts like seals or gaskets, inconsistent pressure can lead to leaks. Scientific molding ensures that parameters are transferable across different machines. If a specific viscosity curve is established during the prototype phase, it can be replicated on a larger press for mass production. This methodology creates a robust process window, reducing scrap rates from an industry average of 3-5% down to under 1% for high-precision components.
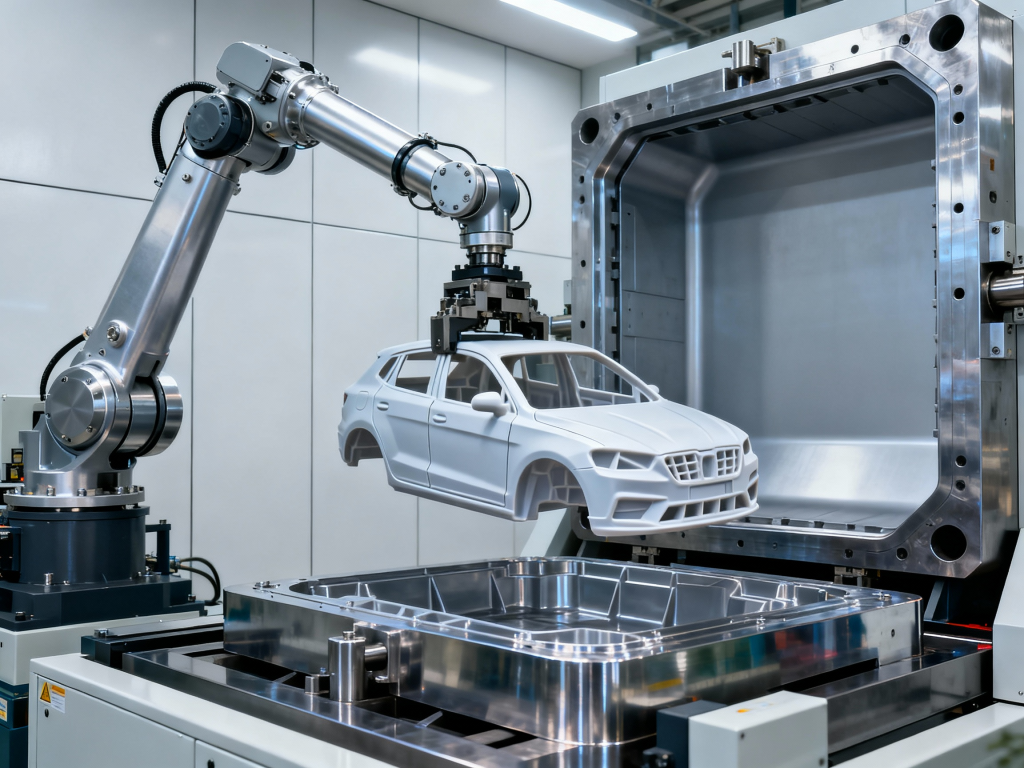

Pre-Production Validation with Moldflow Simulation
Before any metal is cut, digital validation via Moldflow simulation provides a virtual proving ground for automotive injection mold designs. This technology is indispensable for predicting common defects such as gas traps, weld lines, and sink marks, which are detrimental to both structural integrity and aesthetics.
In a recent case involving a large automotive door panel, simulation identified a potential weld line in a highly visible area. By optimizing the gate locations virtually, the engineering team shifted the flow front to move the weld line to a hidden zone, saving roughly $15,000 in potential rework costs. This proactive step ensures that when physical injection molding automotive parts are finally produced, they meet the stringent dimensional tolerances and aesthetic standards required by Tier 1 suppliers immediately off the press.
Livepoint Tooling: Premier Automotive Manufacturing Solutions
Livepoint Tooling delivers end-to-end manufacturing services, seamlessly bridging the gap from rapid prototyping to IATF 16949 certified mass production for global automotive leaders.
IATF 16949 Certified Quality Assurance
Compliance is non-negotiable in the automotive sector. Livepoint operates under strict IATF 16949:2016 and ISO 9001:2015 certifications, ensuring that every component—from EV battery housings to intricate interior trims—meets the rigorous traceability and safety standards required by global OEMs.
From Concept to High-Volume Production
Livepoint excels in accelerating development cycles. They offer rapid tooling solutions using aluminum and soft steel to deliver functional prototypes in as little as 8-12 days. Once validation is complete, their expertise transitions smoothly to high-precision, multi-cavity hardened steel molds capable of supporting millions of cycles.
Advanced Engineering Capabilities
To guarantee zero-defect manufacturing, Livepoint integrates scientific molding principles and comprehensive in-house testing, including CMM inspection and CT scanning. Their facility is equipped to handle complex requirements, including 2K overmolding and insert molding, providing a robust solution for diverse automotive applications.
By combining speed, certified quality, and advanced engineering, Livepoint Tooling stands as a strategic partner for automotive companies aiming to reduce time-to-market without compromising on performance.

